A cable tie (often called a zip tie) might look like a simple piece of plastic. But for procurement managers and engineers, it is a critical fastener that holds global supply chains together.
If you are importing or distributing cable ties, you know that a “general purpose” tie isn’t always the right tool for the job. A standard nylon tie that works perfectly in a server room will snap within months on a solar farm or melt inside a car engine.
For B2B buyers, understanding specific applications helps you stock the right inventory and solve your customers’ problems before they happen. This guide explores the industrial uses of cable ties where performance is non-negotiable.
Automotive and Transportation
Modern vehicles are essentially computers on wheels. A standard passenger car contains anywhere from 1.5 to 3 kilometers of wiring. Cable ties are responsible for keeping these harnesses secure, organized, and away from moving parts.
The Challenge: Heat and Vibration
Under the hood, temperatures fluctuate wildly. Standard Nylon 6.6 can become brittle when exposed to continuous engine heat.
The Solution:
Automotive OEMs use Heat Stabilized Cable Ties. These are engineered to withstand temperatures up to +125°C.
- Vibration resistance: Quality ties must lock securely and not loosen over thousands of miles of road vibration.
- Chemical resistance: They must resist oil, grease, and brake fluids.
Construction and Heavy Industry
On a construction site, cable ties are used for everything from securing safety netting to bundling heavy hydraulic hoses. This environment is rough, dirty, and often exposed to the elements.
The Challenge: UV Radiation
The biggest enemy of outdoor plastic is the sun. Standard white or natural nylon ties absorb UV radiation, which breaks down the molecular structure. In high-sunlight regions, a standard tie can crack and fail in less than three months.
The Solution:
For outdoor projects like solar farms or scaffolding, UV Weather Resistant Cable Ties are mandatory. Carbon black is added to the nylon resin to block UV rays, extending the lifespan of the tie significantly.
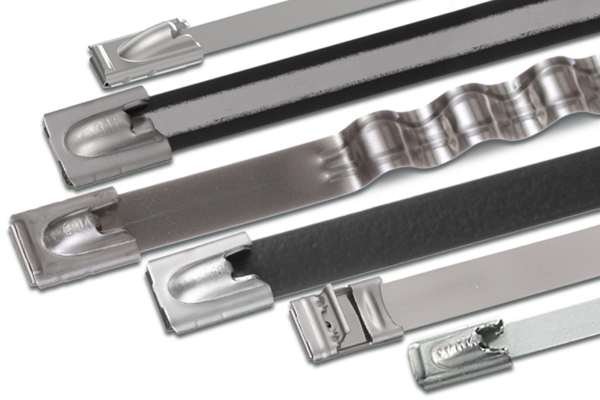
For extreme loads, such as in mining or offshore oil rigs, many engineers switch to Stainless Steel Cable Ties for superior strength and corrosion resistance.

Food Processing and Pharmaceuticals
In food and beverage manufacturing, the priority shifts from strength to safety and hygiene.
The Challenge: Contamination
If a plastic cable tie is cut and falls into a production line (like a batch of dough or frozen vegetables), it can be nearly impossible to find visually. This poses a massive consumer safety risk and can lead to expensive recalls.
The Solution:
The industry relies on Metal Detectable Cable Ties. These ties are infused with metallic particles (usually iron oxide) throughout the nylon.
- Detectability: Industrial metal detectors and X-ray machines can identify even small fragments of these ties.
- Visual Aid: They are typically teal or bright blue to stand out against most food products.
Note: Compliance with safety standards like HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) often requires the use of detectable consumables in production areas. You can read more about HACCP principles on Wikipedia.
Logistics and Inventory Control
Cable ties are not just for bundling; they are also used for identification and security.
- Security Seals: Fixed-length ties act as tamper-evident seals for shipping containers, truck doors, and tote boxes. If the tie is missing or broken upon arrival, the receiver knows to inspect the goods for theft.
- Marker Ties: These feature a flat tag area where users can write or print identification numbers. Warehouses use them to tag equipment, identifying inspection dates or batch numbers without needing adhesive labels that might peel off.

Technical Guide: Matching Material to Application
For distributors, helping your customer choose the right material is a key value-add. Here is a quick reference guide to the most common materials we process at our factory.
| Material | Best Application | Temperature Range | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nylon 6.6 (Standard) | Indoor bundling, office, electronics | -40°C to +85°C | High tensile strength, economical |
| Nylon 6.6 (UV) | Outdoor solar, fencing, gardening | -40°C to +85°C | Resists UV damage for years |
| Nylon 12 | Solar power, extreme climates | -40°C to +85°C | Very low moisture absorption, long life |
| Stainless Steel 316 | Marine, mining, extreme heat | -80°C to +538°C | Fireproof, corrosion-resistant |
| Tefzel (ETFE) | Chemical plants, nuclear, aerospace | -60°C to +170°C | Resists radiation and harsh chemicals |
Why Generic Ties Fail in Industrial Settings
You might see “cheap” ties on the market that look identical to high-performance ones. Why do they snap during installation?
It often comes down to water content and raw material purity.
- Moisture Balance: Nylon is hygroscopic—it needs a certain amount of moisture to remain flexible. If a factory packs ties dry without proper moisture treatment, they become brittle.
- Recycled vs. Virgin Material: Some manufacturers mix recycled plastic (regrind) to cut costs. This compromises the molecular chain, leading to unpredictable breaking points.
At our facility, we use 100% Virgin Nylon 66 for our industrial lines to ensure that the tensile strength listed on the spec sheet is exactly what you get in the container.
Summary
Understanding what cable ties are used for in an industrial context helps you make better purchasing decisions. Whether it’s ensuring a car runs smoothly for 10 years or keeping food production safe, the right tie makes all the difference.
Don’t risk your reputation on a fastener that might fail.
Ready to upgrade your inventory?
We can help you build a product lineup that meets the specific needs of your market, from automotive to heavy construction.
Contact our export team today to request a Free Sample Kit or download our full technical specification sheet.